Best Geospatial Solutions and Services Geospatial Solutions and Services for Every Market Space
The location-based data collection, workflows and analytics life cycle systems, solutions for the market verticals. Best Geospatial Solutions and Services for public and private spatially distributed Infrastructure, Assets based operations and management. The pervasive digital clients have a location data, analytics and data aggregations which optimize business operations.
We provide Cloud, Data Center, on-premise and Hybrid Client-Server System solutions and services. The services includes System Architecture, Design, System migration and System Life-Cycle Development services. We have extensive IT resources to help the client Digital Transformation with Software Development, Operations and management life-cycles.
IT resources to help the client Digital Transformation with Software Development, Operations and management life-cycles.
What are the important Geospatial Solution features for Industry, Trade, Banking and Logistics?
The diverse and connected nature of industries and the increasing Digital Transformation for Industry 4.0. is producing high-volumes of location tagged data stream. The internal systems and stakeholders of Industry, Banks, Insurance, Trade and Logistics sectors is moving away from analog systems to connected digital twin systems.
1. Industry 4.0. Spatial Solutions :
The Industrial IoT and Digital Twin of requires real-time systems with data analytics, workflows and decision support systems. The micro-site sensor data streams and digital twin and metaverse solutions helps the industries to operate fault-free and improve efficiencies.
2. Banking & Insurance Location Analytics:
The physical financial facilities are giving ways for mobile and remote transactions. The distributed local and global mobile banking and consumer spatio-temporal behavior analytics supports banking service delivery operations optimization and management.
3. Trade and Commerce Systems:
The trading and commerce operations are highly dependent on the consumer and market information and fluctuations. The spatial analytics of trade and commerce data byindividual verticals help the companies to optimize operations and maximize financial outcomes.
4. Logistics Geospatial Systems:
The connected vehicles or trucks participating on logistics fleet services industry provide real-time sensor and mobility data with location tags. We provide the best Geospatial Solutions and Services, analytics and value chain analytics for logistics.
GEOSPATIAL MARKET SEGMENTATION MANAGEMENT
It is important to have real-time market intelligence and analytics to finetune the internal operations, logistics and management responses. The market segmentations and analytics helps to formulate agile internal operations that match the ever-changing market conditions and remain sustainable.
- Location: (products/solutions customer location & service-area)
- Market Size: (enough customers to support business response)
- Demographics: (income, age, ethnicity etc)
- Buyer characteristics: (skills, likes, dislikes, favorites, advertisement/media)
- Consumer needs: (features and solutions market requirements)
The breakdowns of market conditions based on field crew and fleet data feeds and market performance helps the businesses to reach better niche of optimization and outcomes.
During the Segmentation Analytics the real-time data feeds are used to define Total Available Market (TAM) and Product/Service Available Markets (P/S-AM) and support client response decisions on Target Market (TM) for
supply side which matches the customer demand.
- Total Available Market- This represents the entire industry the business is operating in. It includes all the different types of customers who are potentially interested in the company’s services. For example, if operating a home-based bakery, the TAM is everyone who is interested in buying baked products. Provide data on the number of prospects in the industry, for example, businesses, households, etc.
- Product/Service Available Market- This is a subset of TAM and represents all the customers that the business can effectively serve. As a home-based bakery, for example, it may not be possible to serve everyone in the country. Therefore, the SAM may need to be defined according to geography. It would be reasonable to sell products to people in nearby towns.
- Target Market- This is a subset of SAM and represents the specific intended customers to serve. For example, it is possible to segment the target market according to criteria such as price (high-priced versus low-priced), quality, geography, occasion (kid’s birthday cakes, pastries for office workers), and others. Ask why the business is selecting a particular target market. By narrowing down on the target market, it will be easier to focus sales and marketing efforts on the type of customers who are most likely to buy the business’ products.
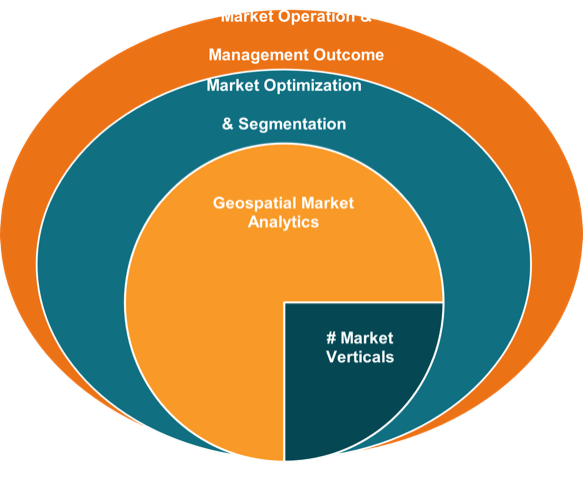
As the businesses by verticals will be able to evaluate the percentage of target market at all times. The Market Share conditions, parameters and business responses are critical for a sustainable financial and stakeholder performance and outcomes. Our solutions use big data, advanced statistics models, AI/ML/DL tools and dashboard to support an agile business management.
COMPETITION
In this section, analyze and dissect the business rivals. Competitive analysis enables the owner to know more about and gain a deeper understanding of the business’ competitors. Make sure that this section describes clearly how the company’s solutions are better for consumers compared to the competitors identified.
Here are some factors to consider when analyzing the competition:
- Direct competitors: When identifying competitors, focus on those who are providing products or services that are similar to the business. How long have they been in business?
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses: Determine what competitors are good at and what they are not offering. Use creativity to identify opportunities that rivals do not have.
- Status quo: Examine the mindset of the other businesses and target customers. Does the business intend to introduce a new idea that will disrupt how things are done?
- Messaging: How will the package of this business’ services overcome the c ompetition?
- Uniqueness: What advantages does the business have over the competition? Why will the company’s service stand out and capture market share?
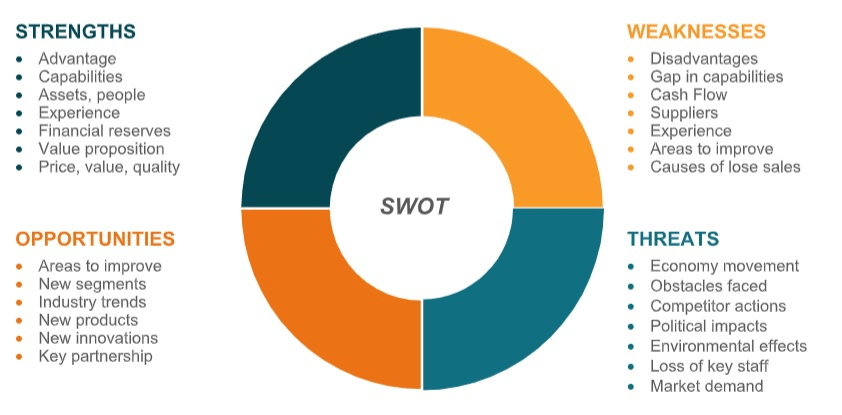
SWOT ANALYSIS
A SWOT analysis is a useful tool for evaluating the business by zooming in on its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities available, and potential threats. Consider the following:
- Strengths: What strengths does the company have now and how will these strengths evolve moving forward?
- Weaknesses: What are the deficiencies in the services? Which areas of the business should be improved first?
- Opportunities: How can the business leverage partnerships and new innovations to grow the business? Which other segments of the industry would the company consider entering in future?
- Threats: How will the package of this business’ services overcome the competition?
Once the SWOT analysis is complete, consider the following aspects of the business:
- How will the business’ strengths help capitalize on available opportunities while minimizing threats?
- How will the business’ weaknesses prevent it from maximizing on these opportunities?
- How will the business’ weaknesses expose it to threats?